elisa test enzyme|enzyme immunoassay vs elisa : vendor An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a specific type of enzyme immunoassay (EIA) that allows for the quantitation of a molecule of interest using antibodies. Antibodies are used to specifically identify the analyte (eg, . We offer a variety of vertical laboratory autoclaves for general purpose sterilization .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Find company research, competitor information, contact details & financial data for Autoclave Canada Corporation of London, ON. Get the latest business insights from Dun & Bradstreet.
ELISA is a common laboratory testing technique that detects and counts certain antibodies, antigens, proteins and hormones in bodily fluid samples. This includes blood, plasma, pee, . Enzyme immunoassays (EIAs) use the catalytic properties of enzymes to detect and quantify immunologic reactions. Enzyme-linked .
anterior posterior labral tear test
An enzyme immunoassay (EIA) or an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a blood or urine analysis that can help diagnose many infections and inflammatory conditions. This is a simple test that does . enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), biochemical procedure in which a signal produced by an enzymatic reaction is used to detect and quantify the amount of a specific substance in a solution. Enzyme-linked .An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a specific type of enzyme immunoassay (EIA) that allows for the quantitation of a molecule of interest using antibodies. Antibodies are used to specifically identify the analyte (eg, .
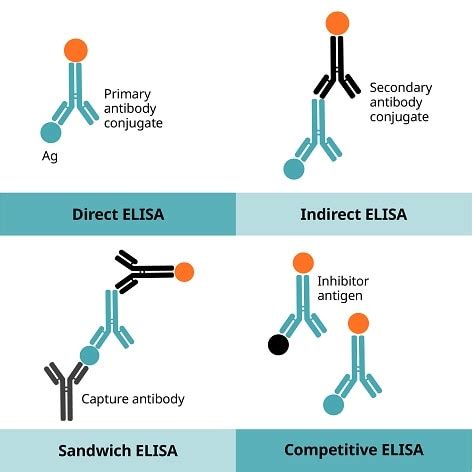
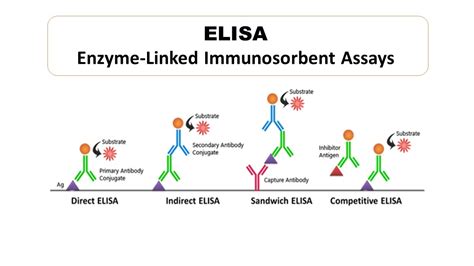
ELISA (enzyme linked immunosorbent assay) is a test performed to detect the presence of antibodies in the blood. Explore the types, procedure, principle and applications of ELISA only at BYJU'S. . ELISA tests can be classified into three types depending upon the different methods used for binding between antigen and antibodies, namely:
anterior talofibular ligament tear test
Enzyme immunoassays (EIAs) use the catalytic properties of enzymes to detect and quantify immunologic reactions. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a heterogeneous EIA technique used in clinical analyses. In this type of assay, one of the reaction components is nonspecifically adsorbed or .Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is an immunological technique extensively used in research and clinical laboratory settings to quantitatively identify a specific protein (i.e., the antigen or biomarker) in a biological matrix while relying on the principle of the specific binding interaction between the antigen and the antibody against the antigen of interest .ELISA stands for enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, also often referred to as enzyme immunoassay (EIA). An ELISA, like other types of immunoassays, relies on antibodies to detect a target antigen using highly specific antibody-antigen interactions. . Possibility to test various sample types: serum, plasma, cellular and tissue extracts, urine . An enzyme conjugated with an antibody reacts with a colorless substrate to generate a colored reaction product. A number of enzymes have been employed for ELISA, including alkaline phosphatase, horseradish peroxidase, and B-galactosidase. Principle of ELISA. ELISA is a plate-based assay technique.
apley test meniscal tear
What is ELISA? ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) is a method used to quantitatively detect an antigen within a sample. An antigen is a toxin or other foreign substance, for example a flu virus or environmental contaminant, that causes the vertebrate immune system to mount a defensive response.
ELISA is so named because the test technique involves using an enzyme system and immunosorbent. ELISA consists of antibodies bonded to enzymes; the enzymes remain able to catalyze a reaction, yielding a visible end product. The term enzyme-linked refers to an enzyme’s covalent binding to an antibody. Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): Enzyme immunoassays, such as the direct ELISA shown here, use an enzyme-antibody conjugate to deliver a detectable substrate to the site of an antigen. The substrate may be a colorless molecule that is converted into a colored end product or an inactive fluorescent molecule that fluoresces after enzyme activation.ELISA is an abbreviation for "enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay." In 1974, P. Perlmann and E. Engvall developed the test as a substitute for certain radioimmunoassay tests, and eventually, it replaced the western blot test for HIV confirmation. The ELISA test is versatile and medical professionals can perform it easily as compared to other more complicated tests; many . The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is an antibody-based technique for the detection and quantification of target analytes in solution. The targets are typically proteins, for example, cytokines, chemokines, immunoglobulins, hormones, and other biomarkers. . If you are establishing your own ELISA, you would have to empirically test .
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) is an immunological technique used for detecting and measuring specific proteins, such as antibodies, antigens, and hormones in biological samples.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay - or ELISA for short - is a laboratory technique or assay where antibodies or antigens in people’s samples are immobilized in a surface, and then detected by an antibody with an enzyme .
The Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) is one of the most sensitive immunoassays available. The typical detection range for an ELISA is 0.1 to 1 fmole or 0.01 ng to 0.1 ng. . General ELISA Test Steps. 1- Prepare .The most common HIV tests use blood to detect HIV infection. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) tests a patient's blood sample for antibodies. Oral fluid (not saliva), collected from the cheeks and gums, may also be used to .
what is elisa used for
what is elisa technique
Der ELISA-Test ist ein Verfahren, bei dem man bestimmte Moleküle in Körperflüssigkeiten nachweisen kann. Man kann zum Beispiel Antikörper oder Antigene nachweisen.. Das Verfahren wird für Viren, Hormone, Medikamente und Gifte angewendet.. Der ELISA-Test wird in verschiedene Formen unterschieden. Dazu gehören der direkte ELISA, der indirekte ELISA .The basic enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), or enzyme immunoassay (EIA), is distinguished from other antibody-based assays because separation of specific and non-specific interactions occurs via serial binding to a solid surface, usually a polystyrene multiwell plate, and because quantitative results can be achieved. .
Engvall E (2010) The ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Clin Chem 56(2):319–320 Engvall E, Perlmann P (1971) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry 8(9):871–874 Hornbeck P (1992) Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays. Curr Protoc Immunol 1:2.1.1–2.1.22
what is an elisa kit
ELISA ELISA - an acronym for Enzyme-Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay. The ELISA assay is a widely used biochemical assay to detect in a sample the presence of and quantity of proteins, such as hormones and antibodies and bacteria or viruses. The ELISA assay uses the coupling of antigens and antibodies and relies on the specificity and affinity of antibodies for antigens.The enzyme -linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is an immunological assay commonly used to measure antibodies, antigens, proteins and glycoproteins in . HIV infection, pregnancy tests, and measurement of cytokines or soluble receptors in cell supernatant or serum . ELISA assays are generally carried out in 96 well plates, allowing multiple . Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a method of quantifying an antigen immobilized on a solid surface. ELISA uses a specific antibody with a covalently coupled enzyme. The amount of antibody that binds the antigen is proportional to the amount of antigen present, which is determined by spectrophotometrically measuring the conversion of .
The basics of ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay), a widely used laboratory technique for detecting and quantifying proteins or antibodies. . Fig: Detection Strategies of ELISA. Types: ELISA tests are categorized into three categories based on the methods applied to bind antigen and antibodies, namely:
ELISA (Enzyme-Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay) is an immunologic technique used to detect the presence and concentration of an antigen or antibody in a sample. The power of an ELISA is based on the extreme specificity of the antigen-antibody interaction. ELISAs have wide-ranging applications, especially as medical diagnostic tools. Figure 1. ELISA . Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays, commonly known as ELISA or EIA is a type of immunoassay and modified version of classic radioimmunoassay i.e., instead of radioisotopes, enzymes have been replaced (considered safe than RIA). For ELISA, a number of enzymes are used, which include alkaline phosphatase, horseradish peroxidase, and β .
In an ELISA test: An enzyme is attached to antibodies; When this enzyme reacts with a certain substrate, a coloured product is formed, causing the solution in the reaction vessel to change colour; If a colour change occurs, this shows that the antigen or antibody of interest is present in the sample being tested (e.g. blood plasma)
apley's test for meniscal tear
apley's test positive meniscus tear
22L 18L 14L Dental Autoclave Steam Sterilizer/Class B Sterilization with Printer
elisa test enzyme|enzyme immunoassay vs elisa